Tajikistan Geography
Mountains cover 93 percent of Tajikistan’s surface area. The two principal ranges, the Pamir and the Alay, give rise to many glacier-fed streams and rivers, which have been used to irrigate farmlands since ancient times. Central Asia’s other major mountain range, the Tian Shan, skirts northern Tajikistan. Mountainous terrain separates Tajikistan’s two population centers, which are in the lowlands of the southern and northern sections of the country.
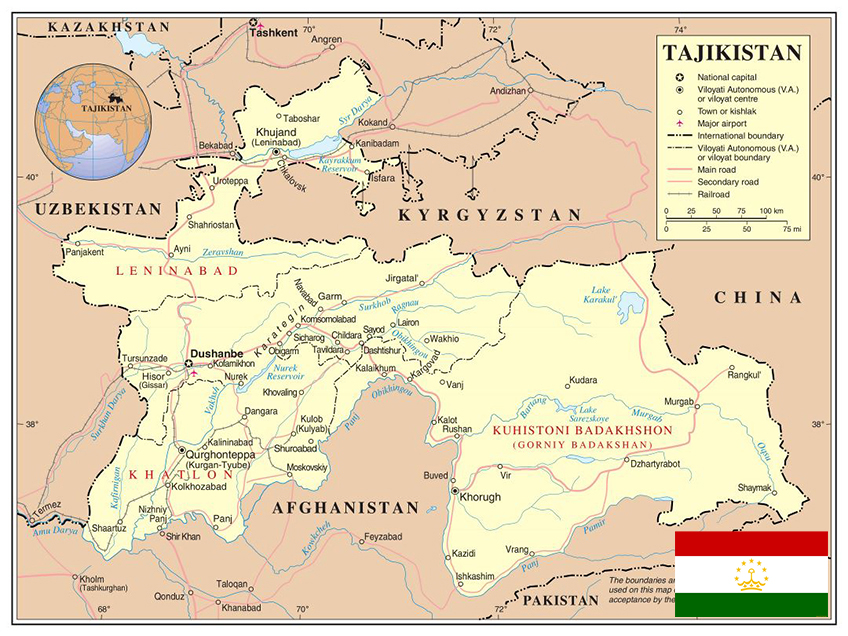
With an area of 143,100 square kilometers, Tajikistan is about the same size as the state of Wisconsin. Its maximum east-to-west extent is 700 kilometers, and its maximum north-to-south extent is 350 kilometers. The country’s highly irregular border is about 3,000 kilometers long, including 430 kilometers along the Chinese border to the east and 1,030 kilometers along the frontiers with Afghanistan to the south. Most of the southern border with Afghanistan is set by the Amu Darya (darya is the Persian word for river) and its tributary the Panj River (Darya-ye Panj), which has headwaters in Afghanistan and Tajikistan. The other neighbors are the former Soviet republics of Uzbekistan (to the west and the north) and Kyrgyzstan (to the north).
Climate
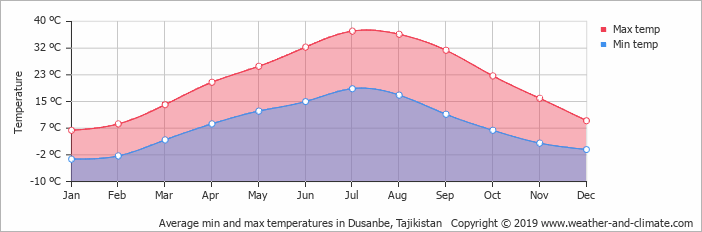
In general, Tajikistan’s climate is continental, subtropical, and semiarid, with some desert areas. The climate changes drastically according to elevation, however. The Fergana Valley and other lowlands are shielded by mountains from Arctic air masses, but temperatures in that region still drop below freezing for more than 100 days a year. In the subtropical southwestern lowlands, which have the highest average temperatures, the climate is arid, although some sections now are irrigated for farming. At Tajikistan’s lower elevations, the average temperature range is 23 ° to 30 ° C in July and – 1 ° to 3 ° in January. In the eastern Pamirs, the average July temperatures is 5 ° to 10 ° C, and the average January temperatures is – 15 ° to – 20 ° C. The average annual precipitation for most of the republic ranges between 700 and 1,600 millimeters. The heaviest precipitation falls are at the Fedchenko Glacier, which averages 2,236 millimeters per year, and the lightest in the eastern Pamirs, which average less than 100 millimeters per year. Most precipitation occurs in the winter and spring.